The Russian Federation and the Popular Republic of China have signed a new Energy Cooperation Agreement that provides for the construction of the Power of Siberia 2 pipeline, a project that could significantly alter the overall natural gas export flow and reinforce bilateral relationship between the two countries.
The initiative takes place amid the economic sanctions imposed on Russia since the beginning of the war in Ukraine in 2022, which caused structural changes in the international energy market.
Until the beginning of the conflict, about 40% of the gas consumed by the European Union was provided by Russia. With the commercial restrictions imposed on Moscow by Western countries, Russian natural gas exports were dramatically reduced.
Data from the period indicate a fall close to 50% in product external sales, with even more significant reductions in oil and coal exports.
The Russian government’s response was to reposition his energy exports to Asian markets, with an emphasis on China. At the same time, Beijing sought to expand his energy security, reduce coal dependence and decrease the vulnerability of his maritime routes, especially those under the influence of the United States and Australia.
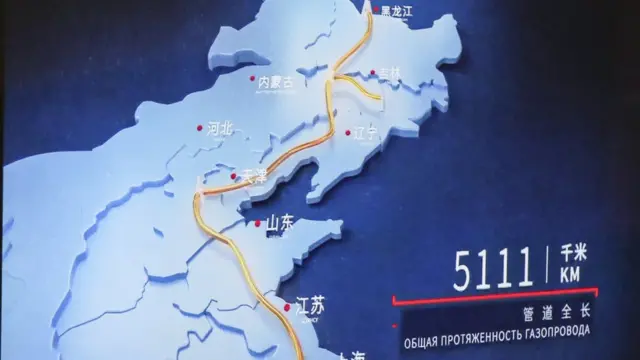
In this context, the Power of Siberia 2 (POS-2) was conceived, pipeline that will connect the gas fields of the Yamal Peninsula, Russia, to the provinces of northern China, through Mongolia.
The project foresees the transportation of up to 50 billion cubic meters of gas per year, with an estimated initial phase of 38 billion cubic meters. The estimate of duration of the agreement is 30 years, which would total about 1.5 trillion cubic meters of natural gas sold over the period.
POS-2 is treated as one of the main ongoing energy infrastructure projects and should alter the geoeconomic balance between Eurasia and the West.
Russian authorities estimate that annual revenue generated with exports may range from US $ 2.5 billion to $ 4.3 billion, values that can significantly impact the economy of Russia’s eastern region by boosting sectors such as infrastructure, transportation and basic industry.
According to technical documents released by the two countries, the pipeline should contribute to the exporting capacity of Russia, while allowing China to diversify its sources of power supply. Partial replacement of natural gas coal is also aligned with Chinese emission reduction commitments, according to environmental multilateral agreements.
In addition to the direct impact on the Chinese energy matrix, POS-2 may change the power dynamics in the international energy market.
Russia’s dependence on the European market tends to be reduced, while China strengthens its position as the main destination for Russian energy exports. The movement also expands Beijing’s bargaining power in future negotiations with Moscow, according to analyzes of institutes specializing in energy policy.
The project still depends on licensing steps and technical definitions. However, authorities involved in the negotiations state that advances in preliminary agreements have already allowed the start of resource mobilization for their implementation.
The government of Mongolia, where it will pass part of the pipeline, also participates in the negotiations to define the route and the terms of operation.
China’s strategic objectives include the search for stability in energy supply and the reduction of dependence on maritime imports, especially those subject to interference in areas of geopolitical tension. The Russian gas terrestrial supply offers a supply alternative considered safer from the logistical and political point of view.
Russia, in turn, uses POS-2 as an alternative to its traditional dependence on the European market, which was strongly compromised after the imposition of economic sanctions related to the Ukrainian conflict. The partnership with China represents, in this sense, a strategic redirection of the West Energy Flow to the East.
Experts point out that the consolidation of this new energy corridor may influence other global supply chains, as well as impacting international natural gas prices. The initiative is closely observed by blocks such as the European Union and by energy exporting countries, which evaluate the developments of the Sino-Russian alliance on the international scene.
POS-2 is part of a broader strategy of both powers to expand its cooperation in areas such as infrastructure, commerce and defense. Although governments have not disclosed detailed deadlines for the completion of the work, official statements signal top priority for the project in the coming years.
The advance of this partnership is interpreted by international observers as an indication of reconfiguration of the global influence poles, especially in the energy sector. The formalization of the project occurs in a transition context in the world energy matrix, with disputes for strategic routes and new sources of supply ongoing.
Source: https://www.ocafezinho.com/2025/05/27/china-e-russia-fecham-parceria-do-seculo-para-construcao-do-maior-gasoduto-do-planeta/

